Overview:
Effective Data Management Services – Inventory Management System:
- Data Governance
- Data Management
- Data Analysis
- Data Quality
- Data Security
- Data Integration
Purpose of Inventory :
Purpose of Inventory :
- To maintain independence of operations
- To meet variation in product demand
- To allow flexibility in product scheduling
- To furnish a safeguard for variation in raw material
- delivery to take benefit of economic purchase order size
- Inventory Systems:
The below are the inventory systems:
• A single period inventory model
• Multiperiod inventory systems
- Inventory Costs:
- Holding costs or carrying costs
- Setup cost or manufacturing cost
- Cost of ordering
- Techniques of Inventory Management:
Some of the major techniques of Inventory management are as follows:
- Economic Order Quantity
- Inventory Models
- ABC Analysis
- Material Requirements Planning
4:Inventory Management:
- Forms of Demand
- Forms of Inventories• Classification of Inventories Cost
- Inventory Control
- Objectives of Inventory Control
- Types of Inventory Management:
Inventory Management deals essentially with balancing the inventory levels. Inventory is categorized into two types based on the demand pattern, which creates the need for inventory. The two types of demand are Independent Demand and Dependent Demand for inventories.
What is Data Management?

Data management includes all of the activities relating to the planning, implementation, development, and control of the information generated by an organization.
In other words, data management is the development and realization of all the processes for the collection, storage, security, quality, dissemination, and changes of data.
From data creation to their retirement, data management is responsible for the end-to-end lifecycle of data.
Typically, data management includes multiple topics and categories such as:
- data security
- data sharing
- data integration
- data governance
- data architecture
- database management
- master data management
- data reference
- business intelligence
- document and record storage
- data quality management
- data warehousing
Data should be treated as a strategic resource. Well-managed data is data in the right place, at the right time, in the right format.
the right time, in the right format.
There are fundamental strategies and best practices for improving the way companies manage their data. We grouped the practices, according to the key categories of data management.
Data Management:
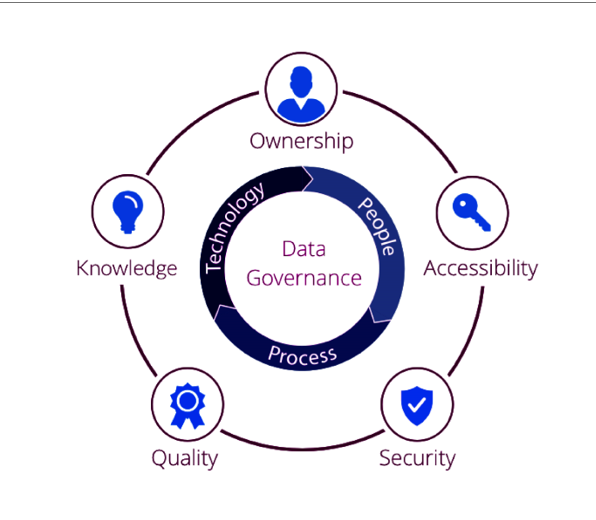
Data Governance and Security:
In short, data governance (DG) includes the management of the usability, availability, consistency, integrity, and security of data in a company.
DG ensures data meet the business rules and standards and thus enable companies to control the management of data resources.
There are many challenges that affect directly the success of your data strategy. From cultural challenges within your organization to political and organizational matters, there are many obstacles you need to face while moving forward with the governance initiatives.
1. Define your data strategy and goals
It is not about a data strategy. It is about a clear and achievable data strategy for your business. A good data strategy requires a deep understanding of your data needs.
There are some key questions you need to know the answer when you are building the strategy:
- What exactly are you trying to achieve? What problem does it solve?
- What are your data needs – where and when?
- When do you need real-time data?
- What data skills and knowledge has your company?
- What is the value of your data? For example, how much one email address worth?
- How do you integrate and transfer data silos?
A well-developed data strategy has a strong data management vision, clear goals, well-defined metrics to measure the success, and a strong business reason.
2. Start small and think of the big picture
DG involves people, processes, and technology solutions.
It is a best practice to start with the people and culture, and then gradually move on to the data governance, stewardship processes, and technology.
You need to suitably design roles and responsibilities and build a team of data managers, including experts from all business areas.
Without the right people, the process will be ineffective.
So, begin with the right people, then define the process, and end by defining and providing the technology.
Never forget the big picture and the big idea. Remember, start with an end in mind.
3. Set the right metrics. Do not measure everything.
Setting the right metrics and focusing on those of them that matter is a whole other science!
Metrics are the core of measuring any progress.
We work in a world where data-driven decision making is what makes your business more effective. Today, we cannot successfully run data management without first identifying the metrics that matter most.
The truth is that you can set metrics to everything related to your data and track different tools available in your company. But, does it worth the efforts?
The best practice here is to identify what the most important metrics are. This way, you would be more focused on optimizing data performance.
Enterprises and businesses that are implementing data management best practices often struggle while developing performance metrics.
Setting the right metrics starts with understanding what your data organizational goals are, and what’s the plan for achieving them.
Choosing the vital key performance indicator( KPIs) is an interactive process that involves feedback from different departments and specialists – e.g. analysts, managers, you!
Thus you will get a better understanding of which data management processes need to be measured and with whom they should be shared.
4. Build effective communication. It is a must.
Do not make data governance full of bureaucracy and never look at communication as something that’s not a real work. To handle DG effectively, communication is just a must.
Managing data governance involves strong communication skills and dealing with different people issues. That’s why effective communication is one of the top gates to success for data governance managers.
How to build an effective communication for DG?
Here are some key points and best practices:
- Introduce your DG program early (even before its launch, if possible) via your most-effective communication channels such as employee emails, meetings, town halls, social media and etc.
- Describe clearly the expected benefits to all involved parties. When all parties see the benefits of a DG, it breaks down barriers to understanding and participation.
- Set clear roles and expectation to the DG team.
- Use jargon-free messages to keep the employees’ attention and understanding.
- Use a wide variety of communication channels such as intranet, emails, any internal social platform, chats and etc.
- Communicate on a regular basis. Develop a timeline and a schedule for your communication activities and channels.
The more you understand and implement communication in DG, the more successful data management efforts will be.
Data Stewardship:
Data is one of the most valuable enterprise assets and must be actively managed.
Data stewardship is the management, collection, use, and storage of data. The goal is to provide businesses with high-quality data that is easily accessible.
Data stewardship involves activities such as creating and managing core metadata (DMBOK); managing data quality issues; documenting standards, guidelines, and rules around data; performing operational data governance activities.
Data stewardship focuses on ensuring that data is treated as an organizational resource.
Here are some important points to help you handle your data stewardship and to maximize the benefits of data stewards work:
5. Data Steward should be a part of the business, not only of the IT
You need to clearly realize that data steward is a business role. Many organizations view data stewardship as an information technology (IT) field. However, it is not only limited to IT.
Most of the data stewardship issues and solutions are linked to business processes or to the business rules. To be truly effective, stewards should be familiarly knowledgeable of the data and its utilization in the business.
The tech interface and background of a data steward is always a preferable advantage, but it is the business knowledge, which is the core. Ultimately, the majority of the root cause analysis tools of data quality are linked to the business.
6. Stewards must have clear and specific goals for data quality progress
Not having well-defined and SMART goals will lead to lack of understanding and less focus.
You, as enterprise or data manager, must define clear goals for data quality improvement based on some relevant and measurable metrics.
When data managers define metrics and targets, make sure the stewards are an integral part of this process.
They must also participate in monitoring the progress and the success of the data quality management and improvements.
7. Stewards should be visible, influential, and accountable
It is not only important for data stewards responsibilities to be well-defined before they start doing their job.
The key moment here is that the stewards should have a fairly high level in the enterprise organization. They need a big vision to understand the impact of data quality on the overall business objectives and success.
Stewards must be empowered to make specific business process shifts and assign assets to address quality problems and situations.
Also, they need the power to influence how their colleagues perform business processes to achieve improvements. Moreover, stewards should be made accountable for data quality improvement.8. Provide the right culture of stewardship
